Introduction to Homesteading: A Path to Self-Sufficiency
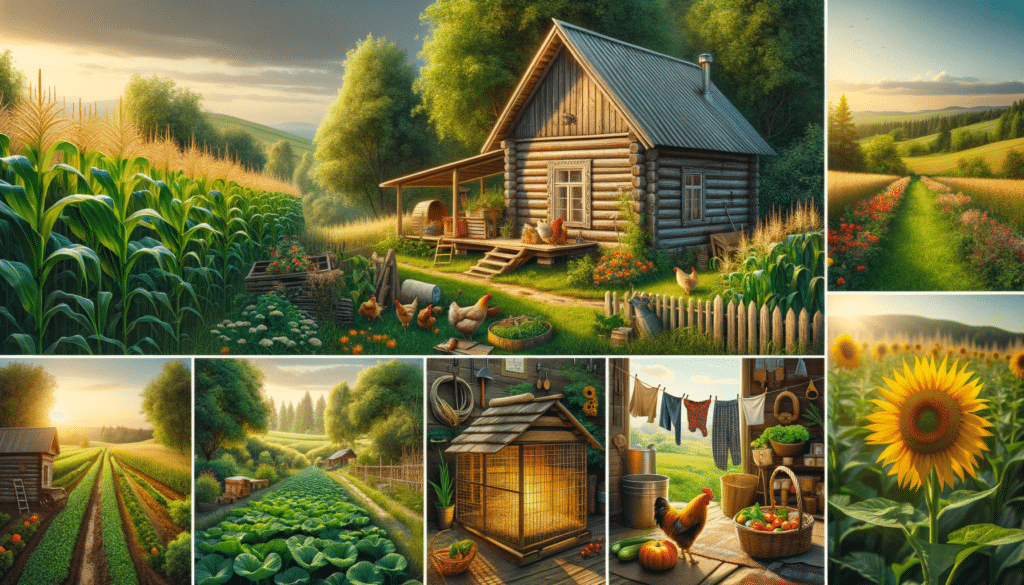
Homesteading represents a lifestyle of self-sufficiency, characterized by growing your own food, raising animals, and living sustainably. This lifestyle choice is becoming increasingly relevant in today’s world, where people are seeking ways to reduce their carbon footprint and live more harmoniously with nature. Historically, homesteading was a necessity for survival, but in the modern era, it has evolved into a conscious choice for many who wish to live independently from the industrialized food system. The movement towards homesteading is not just about survival but about thriving in a way that is mindful of environmental impacts and personal well-being.
The Basics of Homesteading: Skills and Practices
Embarking on a homesteading journey requires a diverse set of skills and practices. At the core of homesteading is the ability to produce food. This includes gardening, where individuals cultivate fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Understanding soil health, crop rotation, and pest management is crucial for successful gardening.
- Gardening: Mastering the art of growing your own produce.
- Animal Husbandry: Raising livestock such as chickens, goats, or bees for eggs, milk, or honey.
- Preservation: Techniques like canning, drying, and fermenting to store food for long periods.
- Renewable Energy: Utilizing solar panels or wind turbines to generate power.
These practices not only provide sustenance but also foster a deep connection with the land. Homesteaders often find joy in the simplicity and satisfaction of their labor, creating a lifestyle that is both fulfilling and sustainable.
Benefits of Homesteading: Health, Environment, and Economy
Homesteading offers numerous benefits that extend beyond mere self-sufficiency. One of the primary advantages is improved health. Consuming fresh, organic produce and engaging in physical activities associated with homesteading contribute to a healthier lifestyle. Moreover, homesteading reduces reliance on processed foods, which are often laden with preservatives and chemicals.
- Environmental Impact: Homesteading promotes sustainable practices, reducing waste and conserving resources.
- Economic Savings: By producing their own food and energy, homesteaders can significantly cut down on expenses.
- Community Building: Many homesteaders engage in local markets and barter systems, strengthening community ties.
These benefits make homesteading an attractive option for those looking to enhance their quality of life while contributing positively to the environment and economy.
Challenges in Homesteading: Overcoming Obstacles
While homesteading offers numerous advantages, it also presents several challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the initial investment in time and resources. Setting up a homestead requires planning, dedication, and a willingness to learn new skills. Additionally, homesteaders must be prepared to face unpredictable factors such as weather conditions and pest infestations.
- Time Commitment: Homesteading is a full-time endeavor that requires ongoing attention and effort.
- Resource Management: Efficient use of water, soil, and energy resources is crucial for sustainability.
- Skill Development: Continuous learning and adaptation are necessary to overcome challenges.
Despite these challenges, many find the rewards of homesteading far outweigh the difficulties, as they gain resilience and independence in the process.
Conclusion: The Future of Homesteading
As the world grapples with environmental concerns and a desire for sustainable living, homesteading stands out as a viable solution for many. It offers a path to self-sufficiency, environmental stewardship, and a deeper connection with nature. While it may not be suitable for everyone, those who embrace homesteading often find a sense of fulfillment and purpose in their lives. As more people seek alternatives to conventional living, homesteading will likely continue to grow, inspiring future generations to live more sustainably and mindfully.